- +91-8010038024
- sales@estmicrowave.com
HALL EFFECT
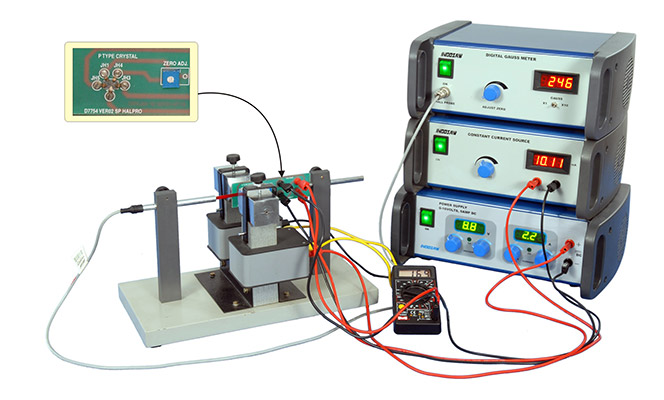
Principle and Working:
When a conductor through which current is flowing, is placed in the magnetic field, a potential difference is generated between two opposite edges of the conductor in the direction mutually perpendicular to both the field and the conductor. This potential developed is Hall voltage & the phenomenon is called Hall effect.
In the present setup, the crystal mount on PCB is placed perpendicular to the pole pieces. Magnetic field is produced by electromagnet operated by 0-16V, 5A power supply. Field intensity measured by gauss meter with radial gauss probe. A constant current is passing through the crystal and hall voltage measured via multimeter.
Exp-1 To determine Hall Voltage (p or n type).
Exp-2 To determine Hall Coefficient.
Exp-3 To determine the type of Charge carrier.
Exp-4 To determine Charge Density of carriers.
Exp-5 To determine the Resistivity of a given sample.
Exp-6 To determine the mobility of charge carriers.
Exp-7 To determine the Hall angle .
Enquiry Now
